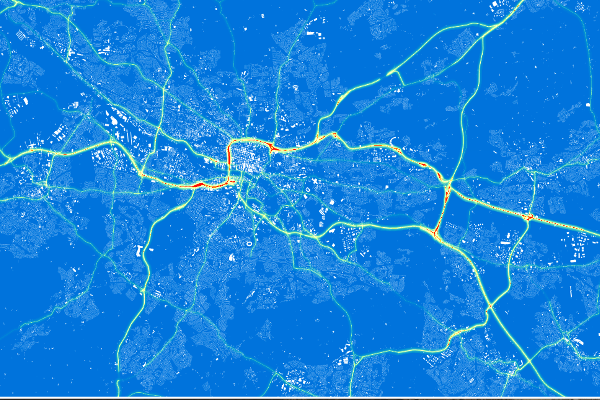
DATA ANALYSIS
It is just as important to have equipment to measure air quality as it is to validate and interpret the data provided by these devices
Data Management and Validation
We are specialists in data management and validation related to air quality, ensuring that the data obtained is accurate, consistent, and compliant with current regulations. Proper data management is essential for effective decision-making and for ensuring that air quality monitoring networks provide reliable information for the protection of public health and the environment.
We offer a rigorous approach to data validation, which includes verifying the quality and reliability of information obtained through automatic and manual monitoring stations. We perform statistical analyses to interpret the information and generate clear and detailed technical reports, essential for the competent authorities and for monitoring the evolution of air quality.
We ensure that all data management and validation processes comply with the highest quality standards, supporting our clients in making decisions based on solid and verified data.
Sensor Validation
The increase in low-cost sensors has opened new opportunities for air quality monitoring, allowing for a broader and more accessible data collection. However, the correct validation of the data obtained from these sensors is essential for their use as a complement to official air quality networks.
At 4sfera, we have extensive experience in validating low-cost sensors and conducting audits to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data they provide. We are experts in verifying that sensor data meets the required quality standards before being used for regulatory purposes or as part of environmental assessments.
We offer comprehensive validation services, ensuring that sensor data is effectively integrated with official network data, allowing it to be trusted for making informed decisions regarding air quality management and public health protection.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
We apply advanced techniques to deepen environmental knowledge through the analysis and interpretation of air quality data. We use official data, sensors, simulation models, and other information sources to conduct assessments at local, regional, and European scales.
To ensure accurate interpretation, we use open-source analysis tools and proprietary software, selecting the best available techniques according to the specific needs of each project.
Additionally, we integrate prediction models and evaluation systems to improve the understanding of air quality and its impact.

Artificial Intelligence
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) allows progress in the analysis and interpretation of environmental data. We have applied AI to predict air quality, fill gaps in time series, and assess data reliability, thus improving the accuracy and usefulness of the available information.
We also use AI to optimize data from air quality sensors, adjusting it through empirical models. This helps correct deviations and ensures that the measurements are more accurate and comparable to official standards.
At the European level, we have collaborated with the European Environment Agency (EEA) in implementing AI to create hourly air quality maps on a continental scale. This work facilitates a better understanding of real-time pollution and assists in decision-making for environmental management.
Air quality forecasting
Air quality forecasting is essential for environmental management at local, regional, national, and international levels. We use advanced atmospheric forecasting models, combining meteorological data, recent air quality analyses, and satellite imagery to anticipate pollution levels.
This task requires specialized experience and knowledge, as pollution forecasting is a complex process dependent on multiple factors. We apply different modeling techniques and use the best available tools to generate accurate short- and medium-term forecasts.
Our forecasts help both public administrations and the general public, offering information to take preventive measures during pollution episodes and improving the ability to respond to adverse environmental situations.